How to Choose Right Metalforming Processes?
At present, the processing methods of metal parts are divided into 7 categories:
1. Casting
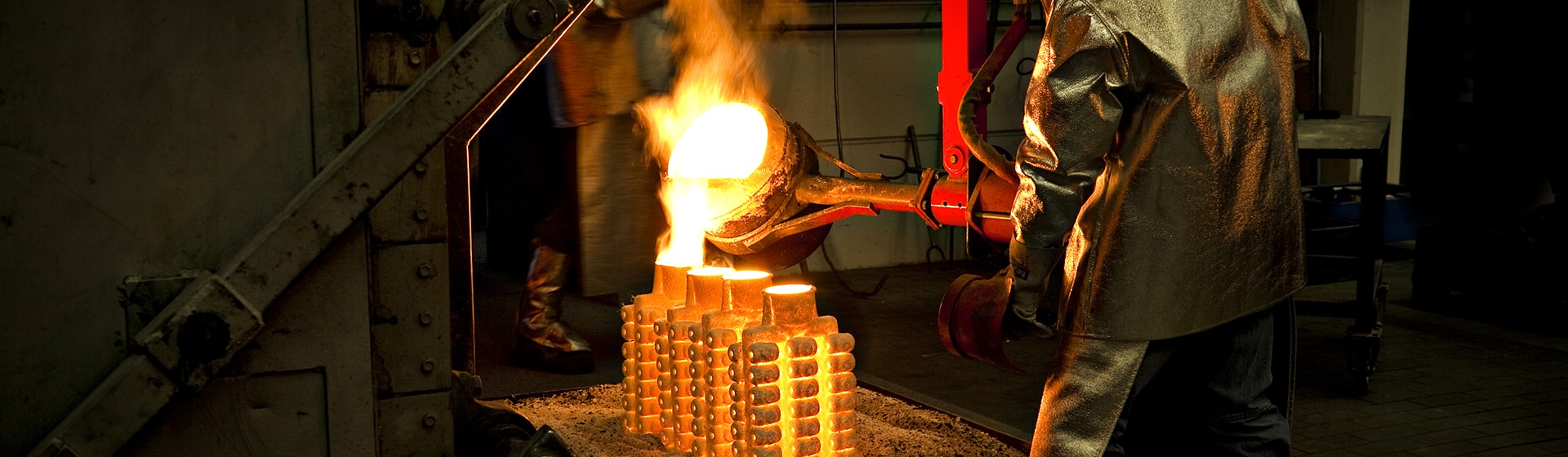

Casting is one of the earliest known methods of metal forming. It generally pours molten metal into a refractory mold cavity and solidifies it. After solidification, the desired finished product is removed from the mold, this processing is known as casting.
After years of development, today’s casting is subdivided into sand casting, investment casting, centrifugal casting, gravity casting, extrusion casting, lost foam casting, etc.
(1) Sand Casting: a casting method for producing castings in sand.
Steel, iron and most non-ferrous alloy castings can be produced by sand casting.
Advantage:
① Suitable for making complex shapes, especially blanks with complex inner cavities.
② Wide adaptability and low cost.
③ For some materials with poor plasticity, such as cast iron, sand casting is the unique forming process for manufacturing its parts or blanks.
(2) Investment Casting: usually refers to making a pattern by fusible material, coating the surface on the pattern with several layers of refractory materials to make a mold shell, and then melting the pattern to obtain the mold without parting surface, which can be filled with sand and poured after high temperature roasting. This process is often referred to as “lost wax casting”. It is suitable for produce small parts with complex shapes, high precision requirements, or difficult to be produced by other processing, such as blades of turbine engines.
Advantage:
① High accuracy in dimensional and geometric.
② High surface roughness.
③ It can make castings with complex shapes, and the alloys materials are not limited.
(3) Centrifugal Casting: It is a casting method in which molten metal is poured into a rotating mold, and the mold is filled and solidified under the action of centrifugal force. Centrifugal casting was first used to produce cast pipes. Centrifugal casting processes are used in metallurgy, mining, transportation, irrigation and drainage machinery, aviation, national defense, automobiles and other industries in domestic and foreign to produce steel, iron and non-ferrous carbon alloy castings. Among them, the castings such as centrifugal cast iron pipes, internal combustion engine cylinder liners and shaft sleeves is the most common.
Advantage:
① There is almost no metal consumption of the gating system and the riser system, which improves the process yield.
②It doesn’t need the cavity core for producing hollow castings, so the metal filling capacity can be greatly improved in the production of long tubular castings, the ratio of the castings wall thickness to the length or diameter can be reduced, and the production process of sleeve and tube castings can be simplified.
③The casting has high density, less defects on pores and slag inclusions, and high mechanical properties.
④It is convenient to manufacture cylinder and sleeve composite metal castings, such as steel-backed copper sleeves, bimetallic rolls, etc. When forming castings, centrifugal motion can be used to improve the metal filling ability, the thin-walled castings can be produced.
(4) Gravity Casting: refers to a molding method in which liquid metal fills a metal mold under the action of gravity, then cools and solidifies in the mold to obtain a casting. Metal mold casting is not only suitable for mass production of non-ferrous alloy castings such as aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys with complex shapes, but also for the production of iron and steel metal castings and ingots.
①The internal pores of aluminum castings are small, and heat treatment can be carried out.
②The cost of the mold is low, and the service life of the mold is long.
③The process is simple and suitable for large-scale operations.
④Special aluminum alloy with low fluidity can be used.
⑤The use of materials is wide.
(5) Lost foam casting (also known as solid casting):Lost foam casting is a process used to create complex metal pieces and parts in which molten metal evaporates a foam mold being held still with sand. The process starts with a polystyrene foam as the mold material which can be carved, machined from a foam block, or created using a process similar to injection molding.. It is suitable for the production of precision castings of various sizes with complex structures, unlimited types of alloys and unlimited production batches. Such as gray cast iron engine case, high manganese steel elbow, etc.
Advantage
①The casting has high precision and no sand core, which reduces the processing time;
②No parting surface, flexible design and high degree of freedom;
③Clean production, no pollution;
④Reduce investment and production costs.
2. Forging
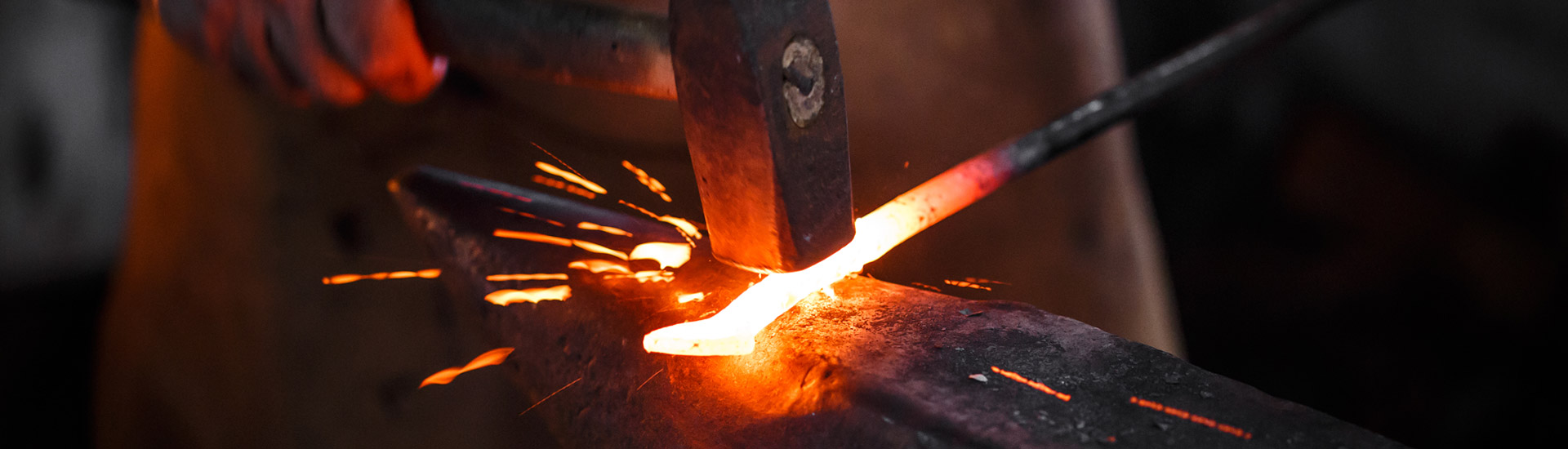

Forging is a processing method that uses a forging machine to apply pressure to the metal blank to plastically deform it to obtain a forging with certain mechanical properties, certain shape and size.
By forging, defects such as as-cast looseness during the metal smelting process can be eliminated, and the microstructure can be optimized. At the same time, due to the preservation of the complete metal streamline, the mechanical properties of forgings are generally better than those of castings in the same material.
According to the forging temperature, forging technology can be divided into hot forging, warm forging and cold forging.
The initial recrystallization temperature of steel is about 727 °C, but 800 °C is generally used as the dividing line, and hot forging is higher than 800 °C; between 300 and 800 °C, it is called warm forging or semi-hot forging; forging at room temperature is called cold forging. Forgings used in most industries are hot forging; warm forging and cold forging are mainly used in automobiles and general machinery, and warm forging and cold forging can effectively save materials.
Forging materials are mainly carbon steel and alloy steel of various compositions, following is aluminum, magnesium, copper, titanium, etc. and their alloys. Iron-based superalloys, nickel-based superalloys, and cobalt-based superalloys are also used for forging or rolling, but these alloys are relatively difficult to forge due to their relatively narrow plastic zone. The heating temperature, opening forging temperature and final forging temperature of different materials have different strict requirements.
3.CNC Machining
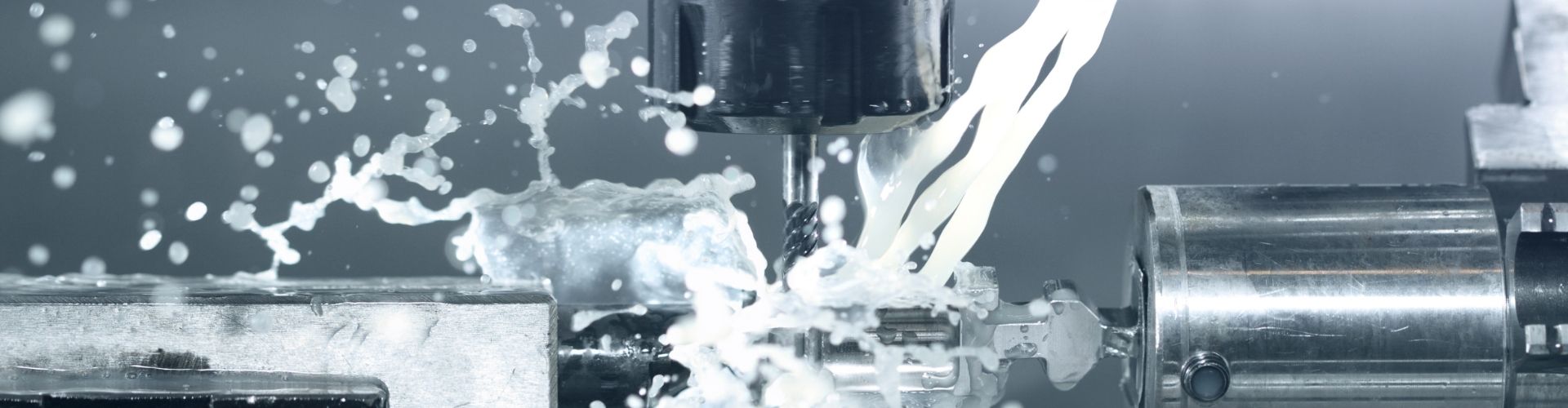

CNC Machining is a process in which the dimensions or properties of a workpiece are changed by mechanical equipment. Common types of machining include turning, milling, drilling, planing, and grinding.
Advantage:
①Machining does not require mold opening, and has a high degree of freedom.
②The precision of machining is very high, which is conducive to improving the quality of the workpiece.
③The machining efficiency is high, which is beneficial to increase the output.
④The use of numerical control operation can reduce production workers and save production costs.
⑤The use of automatic detection and monitoring device is conducive to improving the stability of the workpiece.
4. Sheet Metal
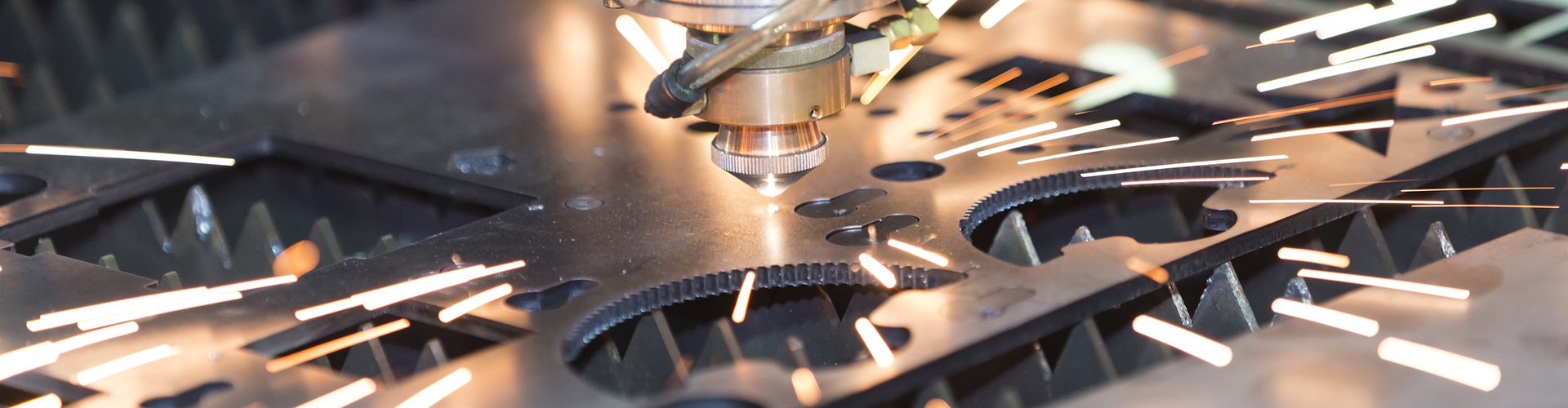

Sheet metal is a comprehensive cold working process for thin metal plate (usually less than 6mm), including shearing, punching/cutting/compounding, folding, riveting, splicing, forming (such as car body), etc. Its remarkable feature is that the thickness of the whole part is same. There are two main methods for sheet metal surface treatment: powder coating and painting. Large pieces are usually choosing powder coating, and small pieces are choosing painting.
Sheet metal processing cutting technology has the advantages of high speed, high precision, high adaptability, fine kerf, small heat-affected zone (small deformation), good quality of cutting end face, no noise in cutting, and welding seam group and performance close to the base metal. Moreover, the processing only requires simple fixtures and no molds, which can replace the processing method of punching and cutting with complex molds, which can greatly shorten the production cycle and reduce production costs.
5. Extrusion
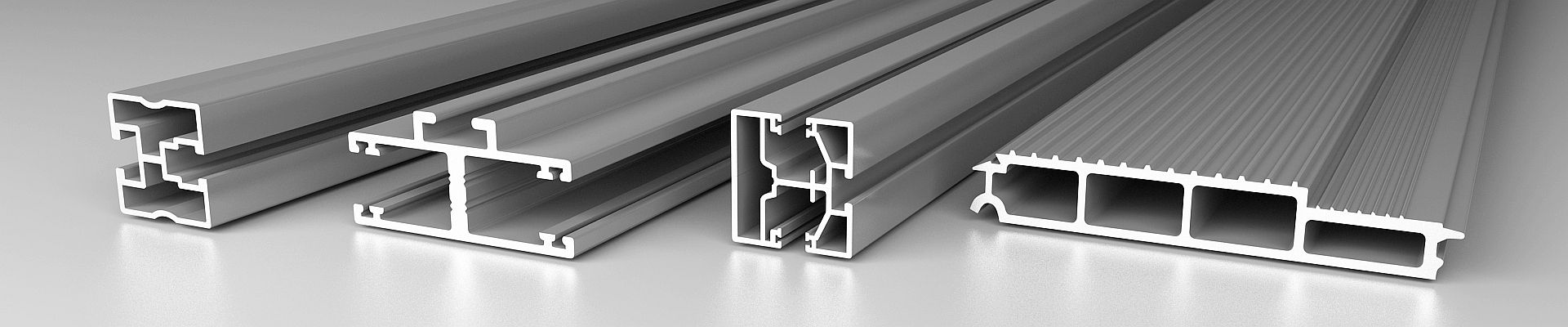
Metal extrusion processing is an important method of using pressure processing principle to make metal forming. Metal ingots are processed into tubes, rods, T-shaped, L-shaped and other profiles at one time by extrusion. Metal extrusion press machine is the most important equipment to realize metal extrusion processing.
The extrusion processing is characterized by the strong three-dimensional compressive stress state, which is beneficial to improve the forming ability of the metal, improve the quality of the product, and improve the internal microstructure and performance of the product. In addition, extrusion processing also has the characteristics of wide application range, large production flexibility, simple process flow and low equipment investment. The most widely used materials for extrusion processing are non-ferrous alloys with low melting point, such as aluminum and aluminum alloys.
6. Cutting
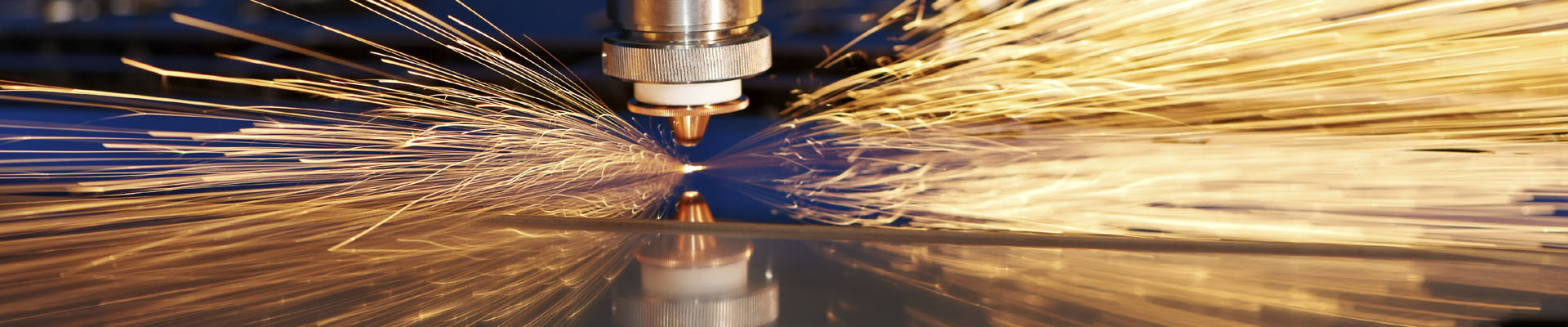

The first step in metal processing is cutting, where the raw material is simply cut or separated by shape to obtain the blanks. Common metal cutting methods are: grinding wheel cutting, saw cutting, flame cutting, plasma cutting, laser cutting and water jet cutting.
①Grinding Wheel Cutting
Steel is cut with high-speed rotating grinding discs. It is the most common cutting method. The grinding wheel cutting machine is light, flexible, simple and convenient to use, and is widely used in various occasions, especially in construction sites and interior decoration. It is mainly used for cutting and processing small-diameter square tubes, round tubes, special-shaped tubes, etc.
② Saw Cutting
The method of dividing a workpiece or material by cutting a slot with a saw blade is called sawing. Cutting materials is the most basic requirement of metal processing, so sawing machines are standard in the machining industry. During the use of the sawing machine, it is necessary to select the appropriate saw blade according to the hardness of the material, and adjust the optimal sawing speed.
③ Flame cutting
The process of flame cutting is a chemical reaction between oxygen and hot steel that heats the metal, softens and melts it. The heating gas is mostly acetylene or natural gas.
Flame cutting can only cut carbon plates, and is not suitable for other types of metals, such as stainless steel, copper and aluminum.
The advantages of flame cutting are low cost and the maximum cutting thickness can reach two meters. The disadvantage is that the heat-affected zone and thermal deformation are relatively large, the section is rough and there is more slag. Considering the subsequent processing, more allowance should be placed.
④Plasma cutting
The plasma cutting method was invented in the 1950s. It is a processing method that uses the heat of a high-temperature plasma arc to locally melt (and evaporate) the metal at the incision of the workpiece, and uses the momentum of high-speed plasma to remove the molten metal to form the incision.
⑤ Laser cutting
Laser cutting is the use of high-energy laser beams to heat, partially melt, and vaporize metals to complete the cutting of materials. It is usually used for efficient and precise cutting of thin steel plates (<30mm).
The quality of laser cutting is excellent, not only the cutting speed is fast, but the dimensional accuracy is also high (up to ±0.05mm), and because the laser beam acts on a very small area, the heat-affected zone is very small, so the workpiece is hardly deformed.
⑥Water jet cutting
Water jet cutting is a processing method that uses high-pressure water to cut metal. With the continuous improvement of technology, garnet, emery and other abrasives are also mixed in high-pressure water to assist cutting to increase the cutting speed and cutting thickness (up to 200mm). The accuracy of water jet cutting can reach ±0.4mm or higher.
7. 3D printing
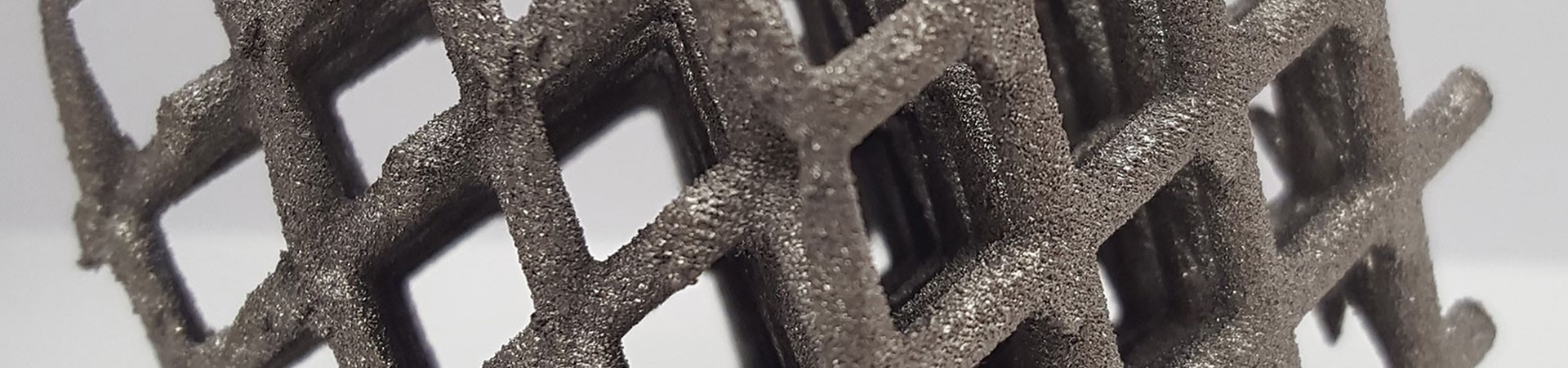

3D printing creates a solid product from a digital model using little more than powdered materials or wire filament. Most products fashioned by 3D printing are more durable, precise, and lightweight, and they’re faster to build than those created by traditional methods.
The process begins by creating a digital blueprint of the object you want to manufacture. You load the printer with the material, for example, plastic filament, wire, or a metal powder. The printer then uses an electron beam or a laser, called selective laser sintering (SLS) or power bed fusion, to heat and fuse the material for production.
As the printer scans the digital model, its print head reproduces the blueprint layer by layer until the object is complete. As the printer creates each layer of material, it cools it into a solid form, and each successive layer adheres to the previous one. 3D printing can make almost any shape through this process with incredible precision.
3D printing focuses on the object’s design and functionality rather than its complexity. Traditional methods like casting and milling can’t equal 3D printing technology’s ability to reproduce complex geometries. 3D printing also allows for almost unlimited design freedom, where a product’s complexity has a limited impact on production cost.
According to above introduction, we know that each process has its own unique advantages, the final choice of which process should be confirmed from the final application of the product, the required performance, order quantity, the accuracy requirements and the cost budget.
If you have the above request, please contact us.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!